Table of Contents
Introduction
As one of the stabilizers for the body, the knees are located between the thighs and legs, allowing flexion and extension. The knees help the hips by supporting the upper body’s weight and allowing the legs to move from one place to another without feeling pain. The knee has various muscles and ligaments surrounding the knee joint, allowing the leg to be bent when active. One of the muscles is located behind the knee, known as the popliteus, and supports the legs. However, minor injuries or actions can affect the knees causing the joint to be in a “lock” position and develop myofascial trigger points that can induce muscle spasms in the knees. Today’s article focuses on the popliteus muscle, how knee pain is associated with trigger points, and how to manage knee pain through various treatments. We refer patients to certified providers that incorporate multiple methods in the lower body extremities, like knee pain treatments correlating to myofascial trigger points, to aid many people dealing with pain symptoms along the popliteus muscles. We encourage and appreciate each patient by referring them to associated medical providers based on their diagnosis, especially when appropriate. We understand that education is an excellent source to asking our providers intricated questions at the patient’s request. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., only utilizes this information as an educational service. Disclaimer
What Is The Popliteus Muscle?
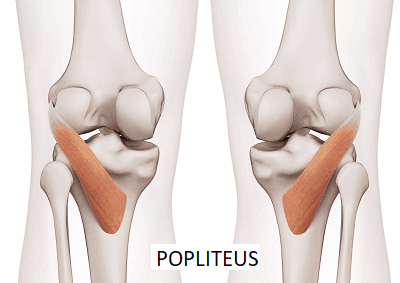
Have you been dealing with pain behind your knees? Do you have issues bending your knees when climbing up or down the stairs? Or do your back knee muscles start to twitch uncontrollably, causing muscle spasms? Many knee issues correlate with various factors that can affect the popliteus muscle and develop trigger points. The popliteus is a small muscle with a very important job as it is a major stabilizing muscle to the knees. The popliteus muscle originates from the lateral side of the femur and inserts itself into the posterior surface of the tibia. Some attachments are between the popliteus and lateral meniscus, allowing the knees to be in motion and providing flexion without pain and entrapment. Additional studies reveal that when a person exercises, the popliteus’s basic function helps bring about and maintain internal rotation of the tibia on the femur. The popliteus also helps prevent the foot from external rotation and allows the individual to stand correctly. However, injuries to the knee could overstretch the popliteus muscle and cause mobility issues to the knee flexion.
Knee Pain Associated With Trigger Points
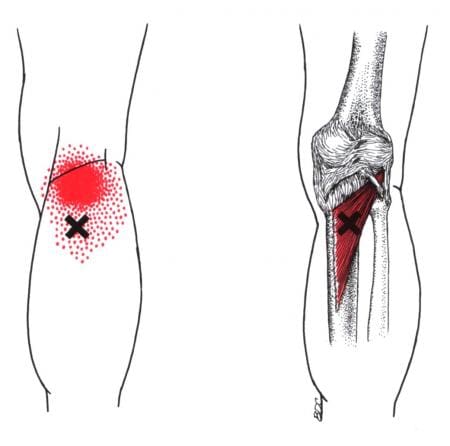
When dealing with knee pain, it could often be a joint disorder like osteoarthritis or a musculoskeletal condition like sciatica pain associated with the knee. These issues could be due to normal factors like constantly sitting down or bending down to lift heavy objects that cause the knees to buckle. However, when the popliteus muscle has been continuously overused from being bent, it can form tiny nodules known as trigger points to cause knee pain. Studies reveal that trigger points on the muscles surrounding the knee are often ignored during a clinical diagnosis. Trigger points cause referred pain to the surrounding muscles, accompanied by various sensory sensations like heaviness, tingling, and hypersensitivity to the popliteus muscle. In “Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction,” written by Dr. Travell, M.D. stated that one of the chief complaints that many patients often talk to their doctors about is the pain they feel in the back of their knees when they are in a crouch position. The book also states when normal actions like running or twisting have overloaded the popliteus muscle, it can cause trauma or strain to the popliteus muscle and tear the posterior cruciate ligament to the knees.
How To Find Trigger Points In The Popliteus- Video
Have you been having knee issues that make walking difficult for a long period? Do you feel like your knees are locking up constantly? What about feeling unstable when standing or carrying objects around? These issues that affect the knees are associated with trigger points along the popliteus muscles. The popliteus muscle is small, located at the back of the knees, and assists with knee flexion. When the popliteus muscle becomes overused, it can cause trigger points to form and cause knee issues. Studies reveal that various issues, like tendon injuries, are associated with repetitive mechanical stresses that can cause degenerative knee lesions. Any trauma or muscle strain can affect the knee’s function of flexing and bending without pain for trigger points to form along the popliteus muscles. The video above focuses on the popliteus muscle, where the trigger points are located, and where the referred pain patterns are situated in the knees. On the bright side, all is not lost, as various treatments offer ways to manage knee pain associated with trigger points.
Managing Knee Pain Through Various Treatments
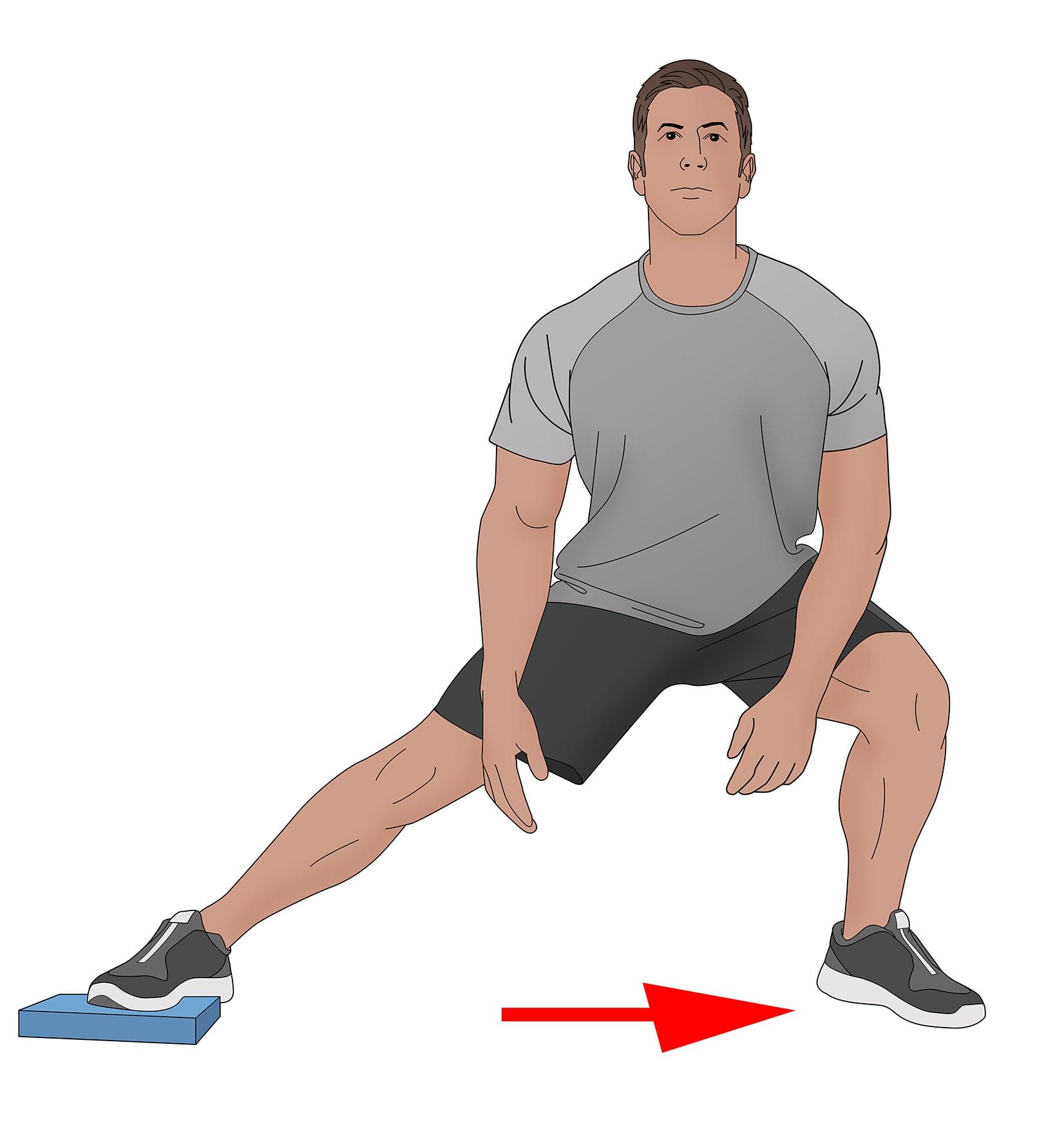
When it comes to knee pain, many individuals will apply an ice or heat compress to allow the surrounding muscles to relax while reducing the pain and swelling. Other individuals use over-the-counter medicines to eliminate the pain for a few hours. While these work at managing knee pain, various treatments target trigger points and can help improve flexion mobility back to the knees. Studies reveal that muscle stretching on the popliteus muscle contributes to joint position sense to knee joint stability and function. Stretching the popliteus muscles can reduce the pain in the back of the knee while elongating the muscle fibers to manage trigger points from forming again. Other treatments that people can do to avoid trigger points from returning is to avoid walking or running in a lateral sloped area to prevent the knees from locking up. Incorporating these treatments to prevent knee issues and allow the knee to function properly.
Conclusion
The knees are one of the stabilizers in the body that are located between the thighs and legs, allowing flexion and extension. As a small muscle located in the back of the knees, the popliteus stabilizes the knees and enables them to be in motion without pain. However, when the popliteus muscle becomes overstretched and overused, it can develop trigger points in the popliteus that invoke referred pain to the surrounding muscles and cause the knees to lock up. To that point, it causes the body to be unstable and mimics knee pain issues. Fortunately, trigger points are treatable through various treatments that help relieve the pain and reduce the trigger points from returning. When these treatments are utilized on the knees, the surrounding muscles regain flexion mobility in the lower body.
References
English, S, and D Perret. “Posterior Knee Pain.” Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 12 June 2010, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2941578/.
Ghaffarinejad, Farahnaz, et al. “Effect of Static Stretching of Muscles Surrounding the Knee on Knee Joint Position Sense.” British Journal of Sports Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Oct. 2007, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2465159/.
Hyland, Scott, and Matthew Varacallo. “Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Popliteus Muscle.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 6 June 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526084/.
Mann, R A, and J L Hagy. “The Popliteus Muscle.” The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Oct. 1977, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/908724/.
Sánchez Romero, Eleuterio A, et al. “Prevalence of Myofascial Trigger Points in Patients with Mild to Moderate Painful Knee Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis.” Journal of Clinical Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 7 Aug. 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7464556/.
Travell, J. G., et al. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual: Vol. 2:the Lower Extremities. Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
Disclaimer
General Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Having Unquestionable Knee Pain? Could Be Trigger Points" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multistate
Multistate Compact RN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics




















